The history of Ladakh reveals a land nestled in the northernmost part of India, known for its rugged beauty and rich cultural heritage. From its early days as a center of ancient trade routes to its modern status as a Union Territory and adventure tourism hub, Ladakh’s story is one of resilience and cultural fusion. In this blog post, we’ll take a deep dive into the fascinating history of Ladakh, exploring its journey from an ancient kingdom to a destination popular with modern-day travelers.
Introduction to Ladakh’s Historical Significance
Ladakh, often called the “Land of High Passes,” is renowned for its stark landscapes, high-altitude deserts, and snow-clad peaks. However, its historical significance goes far beyond its natural beauty. Over centuries, Ladakh has been a melting pot of various cultures and empires, each leaving a distinct imprint on its culture, religion, and architecture.
This region has been a crossroads for trade and cultural exchanges, shaped by its proximity to Tibet, Central Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. Understanding Ladakh’s history offers valuable insights into the blend of traditions and influences that make this place so unique.
Early Civilizations of Ladakh: The Roots of an Ancient Kingdom
The early history of Ladakh dates back over two millennia. Archaeological evidence suggests that the region was home to several early civilizations, possibly influenced by its proximity to the Indus Valley. These ancient settlers adapted to the harsh, arid climate and established small, self-sustaining communities along river valleys.
The Role of Geography in Ladakh’s Development
Ladakh’s geography, dominated by the Himalayas and the Karakoram ranges, played a crucial role in shaping its history. The region’s isolation helped preserve its unique culture but also made it a strategic point for empires looking to control trade routes. Ladakh’s harsh, high-altitude terrain made it difficult to conquer, yet it became a significant link in the ancient Silk Road.
Influence of Ancient Trade Routes and the Silk Road
Ladakh’s position along the ancient Silk Route made it an essential hub for traders moving between Central Asia, Tibet, and India. Goods like silk, spices, and precious stones passed through Ladakh’s valleys, enriching the local economy and fostering cultural exchange. Many of Ladakh’s oldest settlements, including Leh and Zanskar, were once bustling centers for merchants. The influence of these ancient trade routes is still evident in the region’s rich tapestry of cultures and traditions.
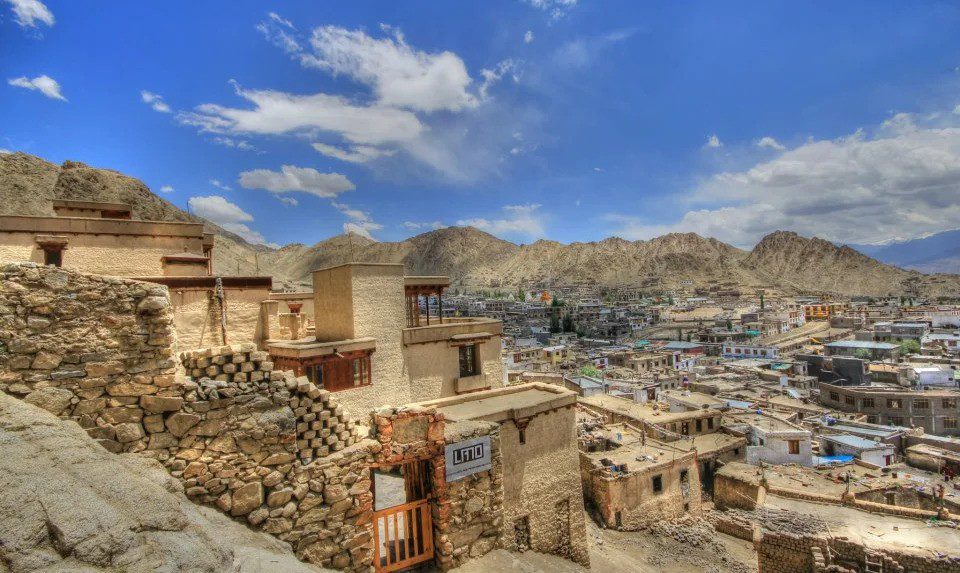

Ladakh Under the Namgyal Dynasty
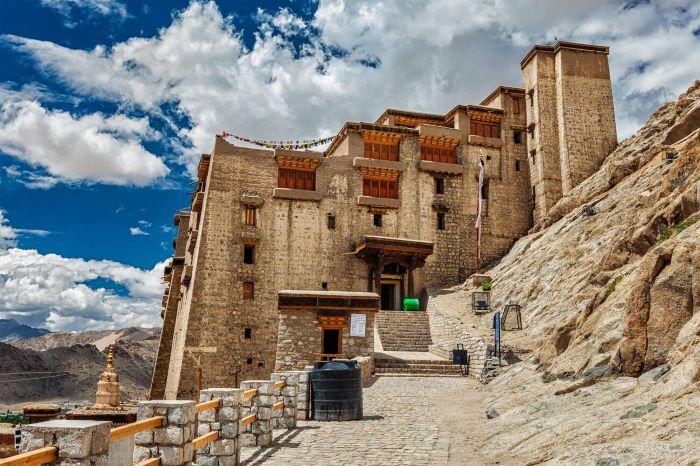
Ladakh’s political history reached its peak during the reign of the Namgyal dynasty, which ruled the region from the 10th century until the mid-19th century. The Namgyal kings were instrumental in unifying Ladakh and establishing it as an independent kingdom, with Leh as its capital.
The Rise of the Namgyal Dynasty
The Namgyal dynasty rose to prominence by defeating several smaller regional powers and establishing a centralized kingdom. The most famous ruler, Sengge Namgyal, built many of the architectural landmarks still visible in Ladakh today, including the Leh Palace. This dynasty fostered ties with Tibet, leading to the widespread adoption of Tibetan Buddhism, which still influences the region.
Ladakh’s Defense Against External Forces
Throughout its history, Ladakh has been a target for various external powers. The Namgyal kings were forced to defend their kingdom from invasions by the Mughals, Tibetans, and Dogras. Despite periods of conflict, Ladakh managed to retain much of its autonomy by forging strategic alliances. The Indo-Tibetan relations during this period also brought spiritual and cultural exchanges, further strengthening the region’s Buddhist identity.
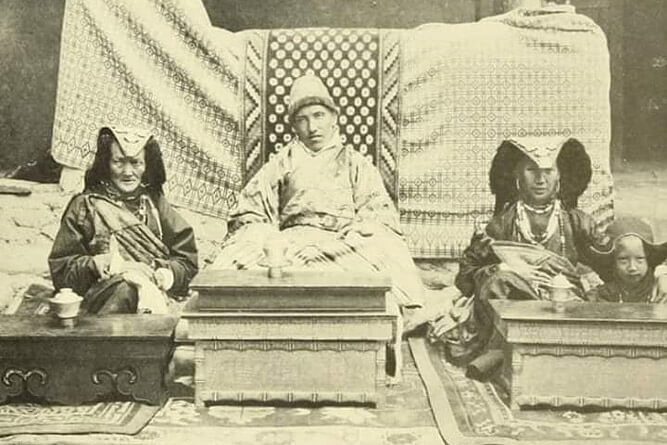

The Spread of Tibetan Buddhism in Ladakh
Buddhism has been a cornerstone of Ladakh’s cultural and spiritual life since the 7th century. The region’s religious heritage is heavily influenced by Tibetan Buddhism, which has shaped everything from Ladakh’s monasteries to its annual festivals.
Monasteries and Gompas: Centers of Power and Culture
Ladakh is home to some of the most significant Buddhist monasteries in the world. Iconic structures such as Hemis Monastery, Thiksey Monastery, and Alchi Gompa serve not only as places of worship but also as centers for cultural preservation. These gompas house priceless Buddhist texts, artworks, and relics. Monastic festivals like Hemis Tsechu attract thousands of visitors, providing a window into Ladakh’s deep-rooted Buddhist traditions.
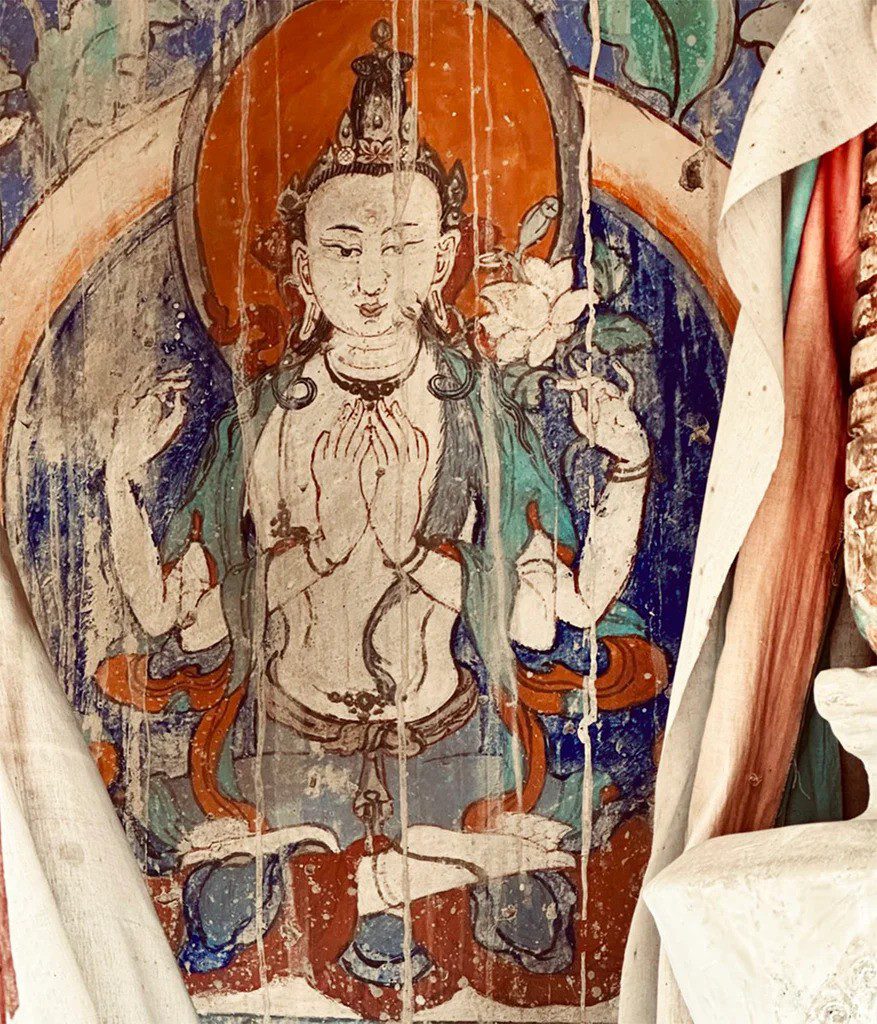
Impact of Buddhism on Ladakh’s Art and Architecture
The influence of Tibetan Buddhism is evident in Ladakh’s distinct art and architecture. The region’s monasteries feature intricate murals, ancient thangkas (Buddhist paintings), and towering statues of deities. Ladakh’s ancient architecture, often constructed from mud bricks and timber, reflects Tibetan designs adapted to the high-altitude environment.

Ladakh Under External Powers: Mughal and Dogra Rule
While the Namgyal dynasty was largely successful in defending Ladakh’s independence, the region eventually came under the influence of external powers, including the Mughal Empire and the Dogra rulers of Jammu.
Ladakh’s Political Shifts During Mughal Rule
In the 17th century, Ladakh faced increasing pressure from the Mughal Empire. After a series of conflicts, the Namgyal rulers agreed to pay tribute to the Mughals while retaining internal autonomy. This period marked a delicate balance between maintaining independence and managing external influences.
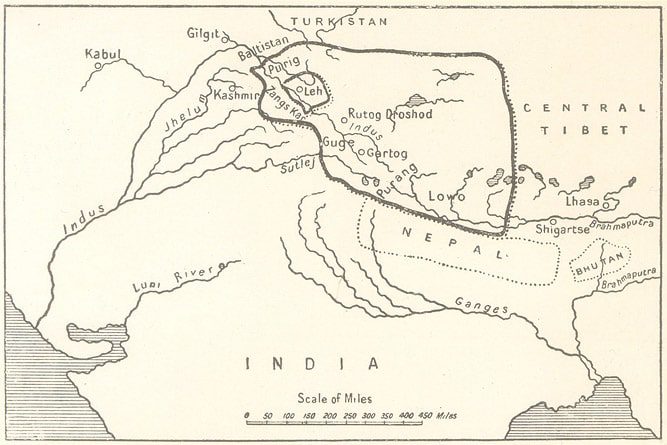
Integration into Jammu and Kashmir
In the mid-19th century, Ladakh was annexed by the Dogra rulers of Jammu, becoming part of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. This political shift fundamentally altered Ladakh’s status, although the region retained much of its cultural autonomy.
Post-Independence Ladakh: From 1947 to Union Territory Status
After India gained independence in 1947, Ladakh became a part of the newly formed state of Jammu and Kashmir. However, the region’s strategic importance grew significantly due to its proximity to both China and Pakistan.
Ladakh’s Role in Indo-China Border Conflicts
Ladakh’s location along the contested Indo-China border has made it a flashpoint in several conflicts, including the Sino-Indian War of 1962. Even today, the region remains strategically important, with Indian and Chinese troops stationed along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
Modern-Day Ladakh: Becoming a Union Territory
In August 2019, the Indian government restructured the state of Jammu and Kashmir, making Ladakh a separate Union Territory. This move has provided Ladakh with greater political autonomy and has boosted the region’s development, particularly in the tourism sector.
Ladakh’s Transformation into an Adventure Hub
While Ladakh’s history is deeply rooted in its ancient past, the region has transformed into one of India’s premier adventure tourism destinations. Its unique landscapes, coupled with opportunities for trekking, mountaineering, and cultural exploration, have attracted travelers from around the world.
Adventure Tourism in Ladakh: A Booming Industry
The rugged terrain of Ladakh provides the perfect backdrop for adventure enthusiasts. Activities like trekking in Zanskar, white-water rafting on the Indus River, and mountaineering in the Stok Kangri range have made Ladakh a global adventure hub. The region’s growing popularity among thrill-seekers has played a crucial role in its economic development.
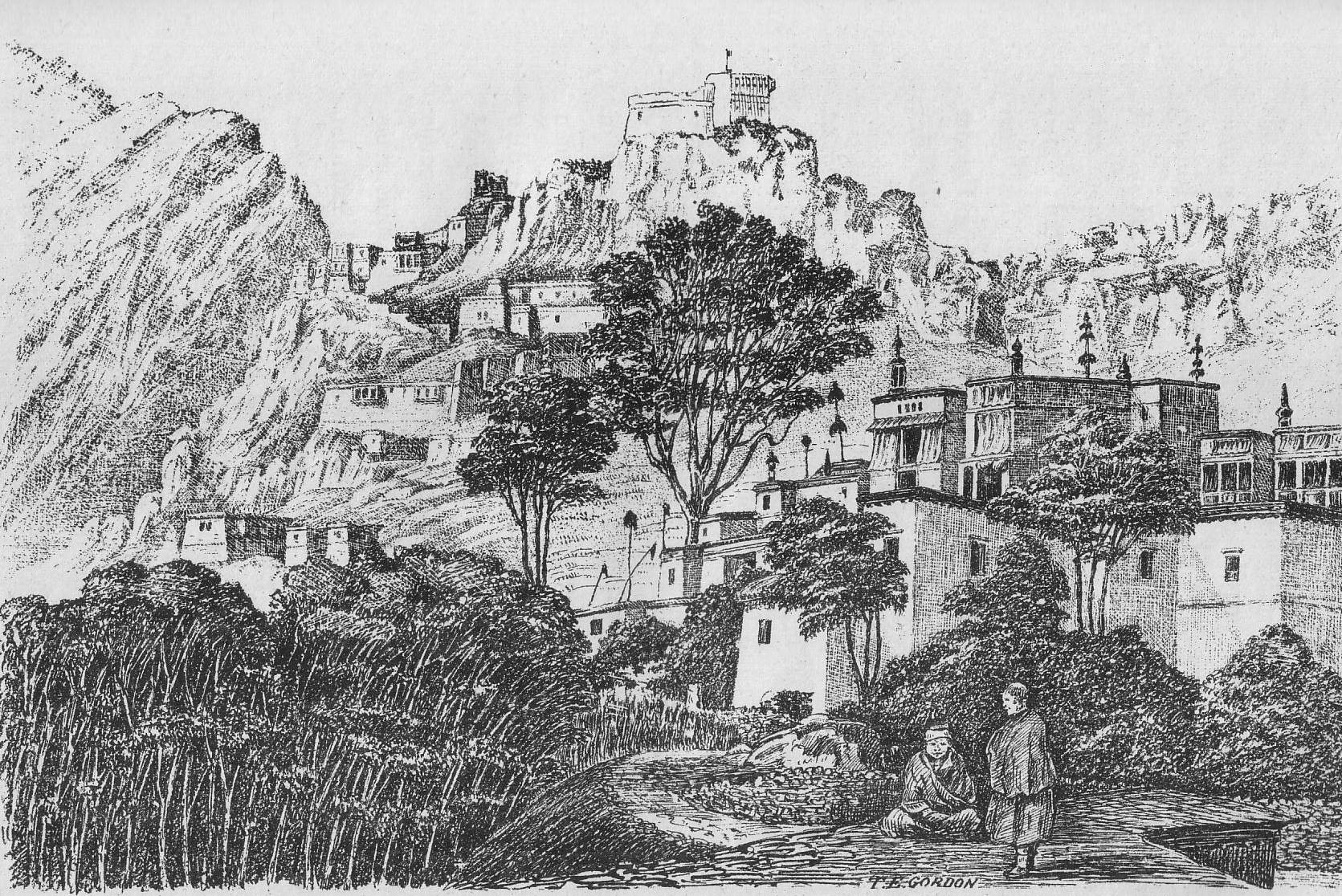
Historical Landmarks in Ladakh Popular with Tourists
Many of Ladakh’s historical landmarks have become key attractions for tourists. Leh Palace, once the residence of Ladakh’s royal family, and Shey Palace, the ancient seat of Ladakhi kings, offer glimpses into the region’s regal past. Other notable sites include the Alchi Monastery and the iconic Pangong Lake, which draw visitors seeking both history and natural beauty.

Cultural Heritage of Ladakh in the Modern Era
Despite its modernization and growing tourism industry, Ladakh has managed to preserve much of its cultural heritage. Ancient festivals, religious practices, and traditional crafts continue to thrive, offering visitors an authentic experience of Ladakh’s rich history.
Preservation of Ladakh’s Festivals and Traditions
Festivals like Losar (New Year) and Hemis Tsechu (a Buddhist festival) continue to be celebrated with great enthusiasm. These festivals are not only religious observances but also opportunities for Ladakhis to showcase their vibrant culture through dance, music, and traditional attire.
Sustainability and Cultural Tourism in Ladakh
Ladakh’s government and local communities have placed increasing emphasis on sustainable tourism. Efforts to protect the region’s fragile ecosystem while promoting cultural tourism aim to strike a balance between growth and preservation.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Ladakh
From its early days as a vital link on the Silk Route to its current status as a Union Territory and adventure hub, Ladakh’s history is a testament to its resilience and cultural diversity. The region has preserved its ancient traditions while embracing modernity, making it a destination like no other. Whether you are drawn by its spiritual heritage, stunning landscapes, or thrilling adventures, Ladakh’s story will captivate your heart and mind.

Q&A Section
1. What is the significance of Ladakh in ancient trade?
Ladakh was a crucial stop on the ancient Silk Route, connecting Central Asia, Tibet, and India. Its location facilitated trade and cultural exchange, shaping the region’s history and economy.
2. Who were the Namgyal rulers of Ladakh?
The Namgyal dynasty ruled Ladakh from the 10th to the 19th century. They unified the region, promoted Tibetan Buddhism, and built many of the region’s significant architectural landmarks, including Leh Palace.
3. How did Tibetan Buddhism influence Ladakh’s culture?
Tibetan Buddhism became the dominant religion in Ladakh, influencing its art, architecture, and festivals. Monasteries and gompas became centers of cultural and spiritual life in the region.
4. What role did Ladakh play in Indo-China conflicts?
Ladakh has been a focal point in border disputes between India and China, including the 1962 Sino-Indian War. Its strategic location makes it a critical area for both countries.
5. How did Ladakh become a Union Territory?
In August 2019, Ladakh was separated from Jammu and Kashmir and became a Union Territory, giving it greater political autonomy and encouraging regional development.
6. What makes Ladakh a popular adventure tourism destination?
Ladakh’s rugged terrain, high-altitude treks, and stunning natural landscapes make it a popular destination for adventure enthusiasts, offering activities like trekking, mountaineering, and rafting.








