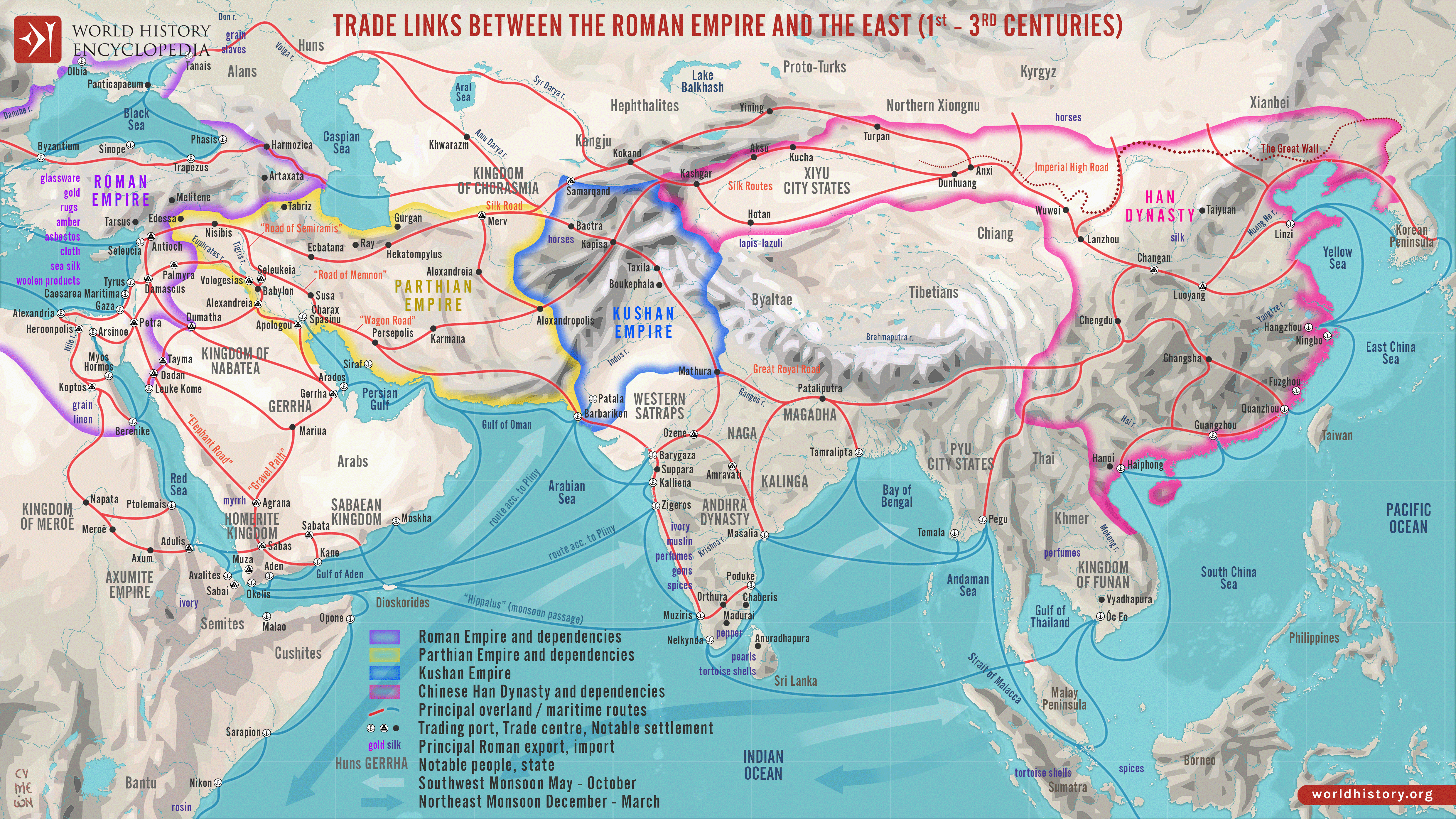
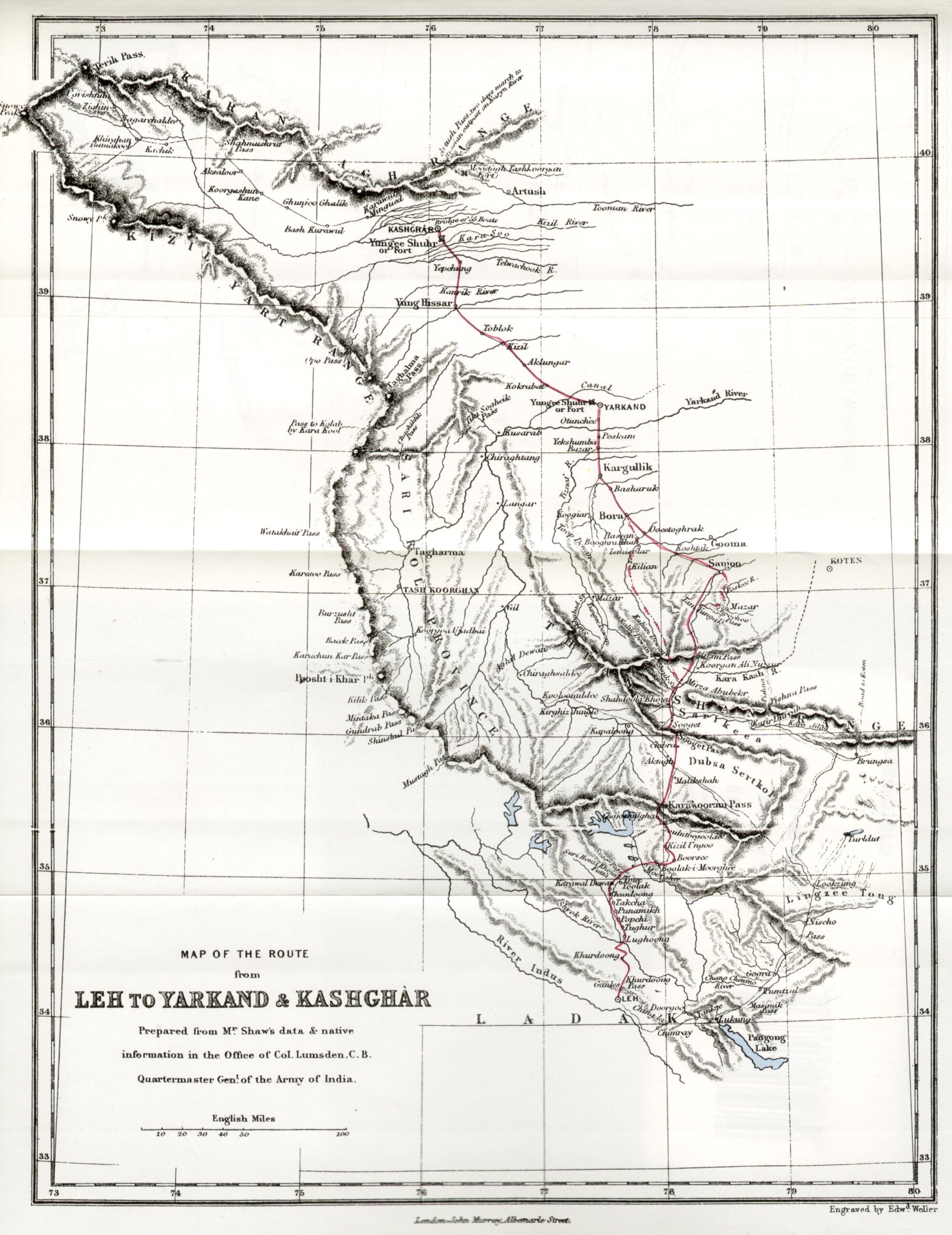
The ancient trade routes of Ladakh are a captivating story of commerce, culture, and survival. Once a bustling hub on the legendary Silk Road, Ladakh connected India with Central Asia, weaving together a network of mountain passes, valleys, and plateaus that facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and traditions. Today, these routes remain a testament to Ladakh’s enduring legacy as a crossroads of civilizations.
Ladakh, often referred to as the “Land of High Passes,” was a vital link in the trans-Himalayan trade network. Traders journeyed through its steep mountains and perilous passes to exchange luxury goods like silk, spices, and precious stones. Its strategic location between Central Asia, Tibet, and India made it an indispensable part of the Silk Road.
Ladakh’s challenging geography both enabled and constrained trade. Its towering mountain ranges, such as the Karakoram and Zanskar, created natural barriers but also served as conduits for trade. Key geographic features include:
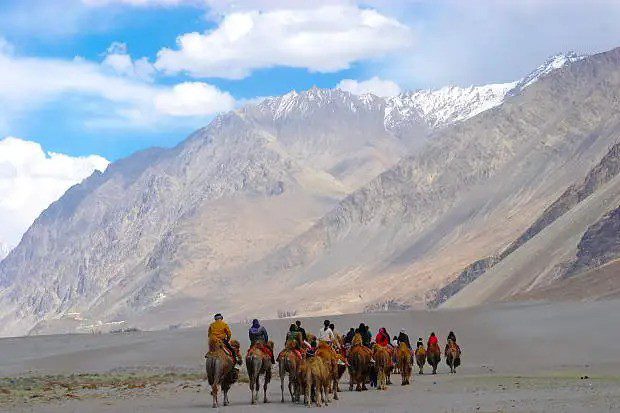
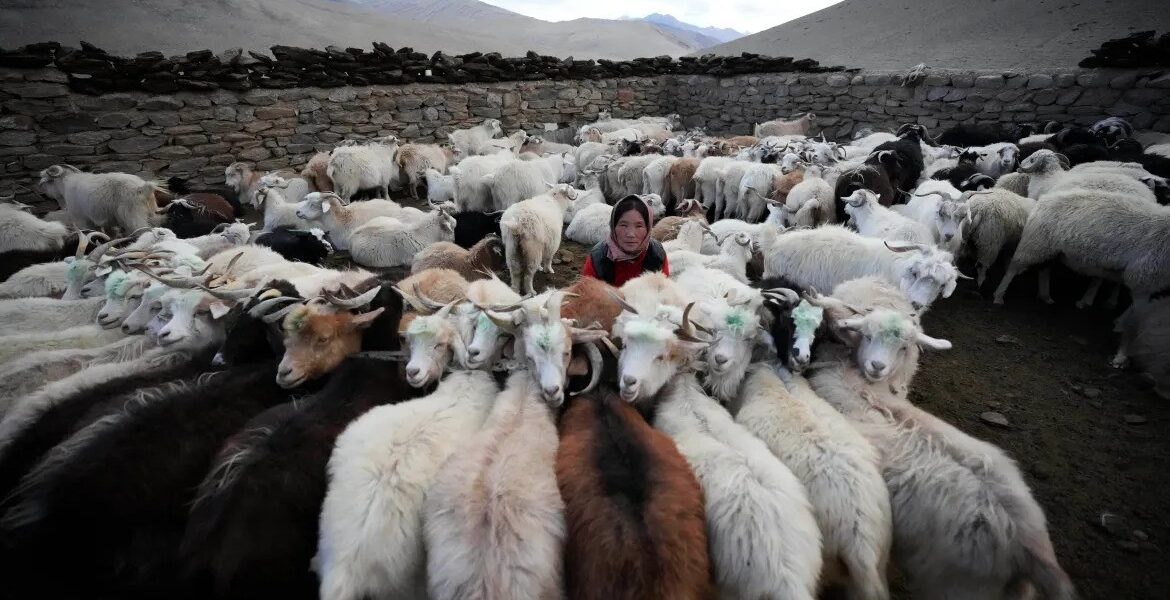
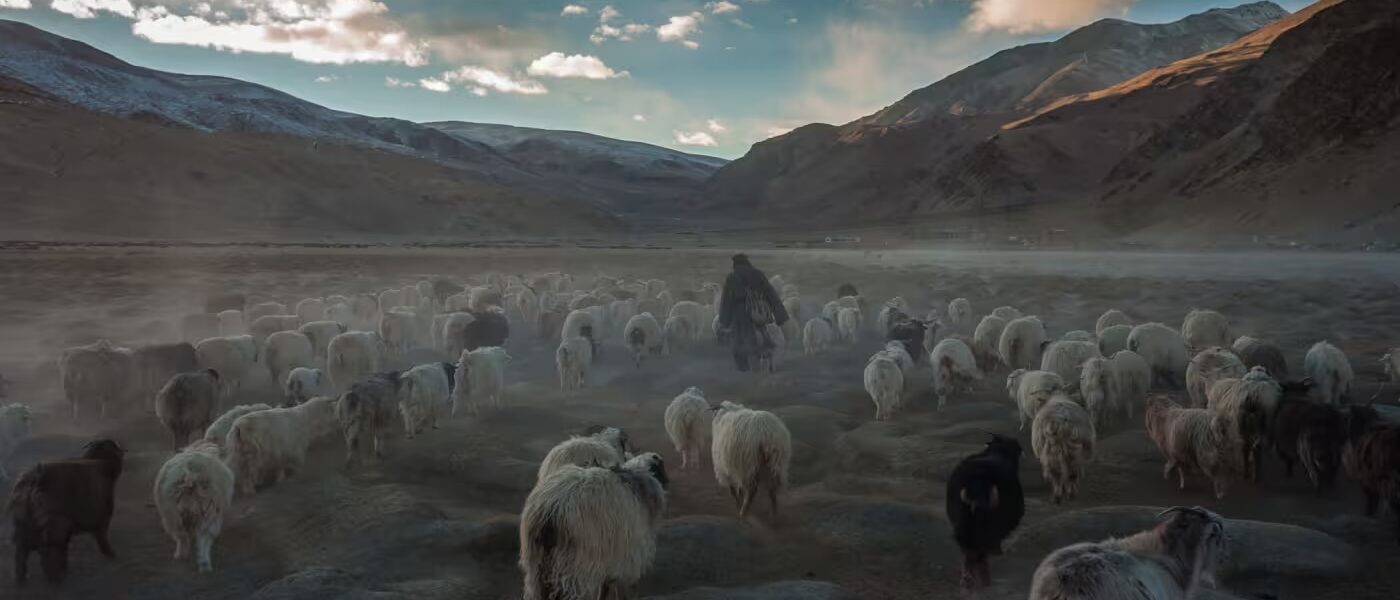
The Nubra Valley was a vital artery for trade. It connected Leh to Central Asia through the Siachen Glacier and the Karakoram Pass. Caravans carrying silk, wool, and spices often rested in Panamik, a village famous for its hot springs.
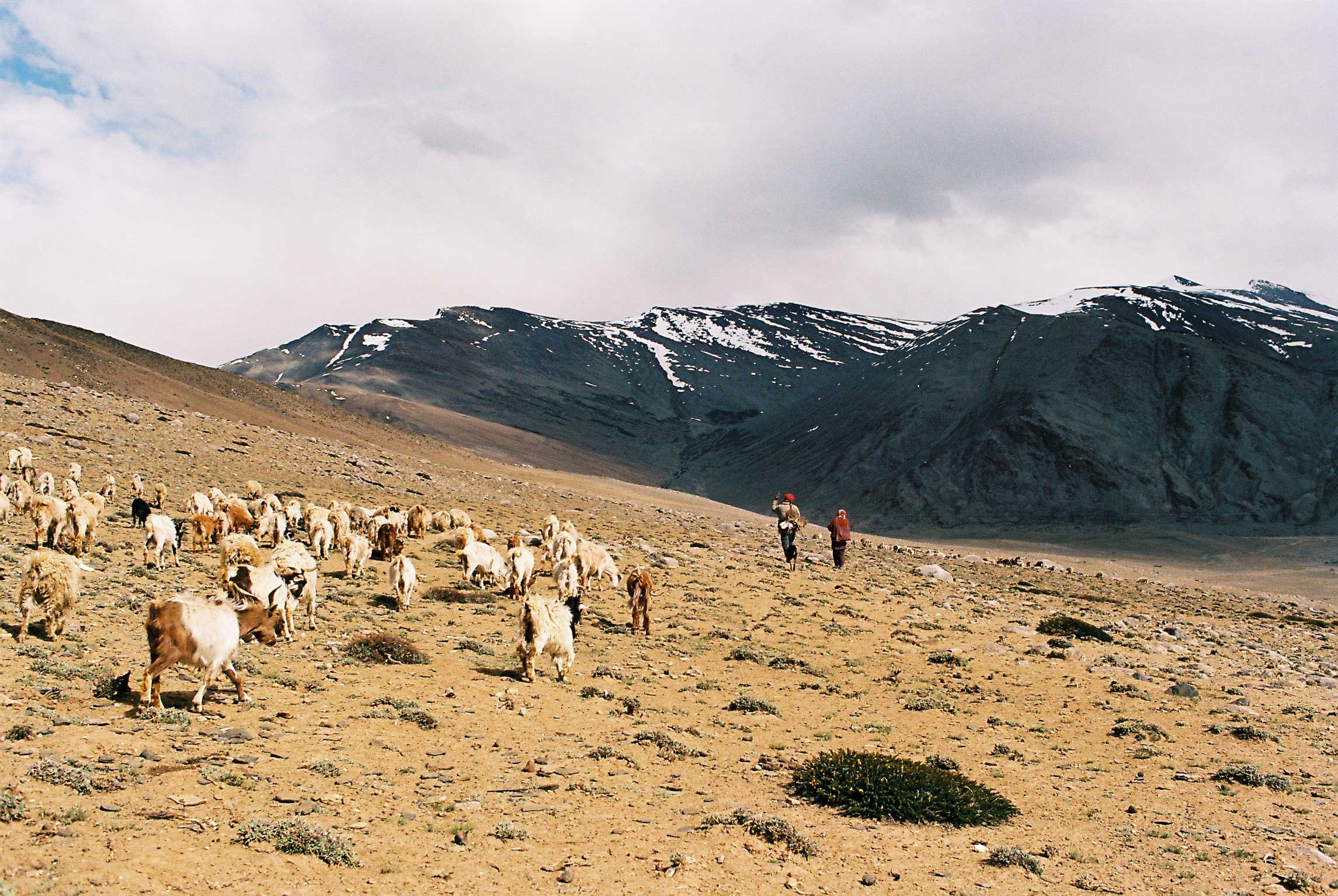
The Changthang Plateau, inhabited by nomadic herders, served as a lesser-known route to Tibet. Traders would traverse this plateau with yaks laden with goods, exchanging wool and salt for tea and textiles.
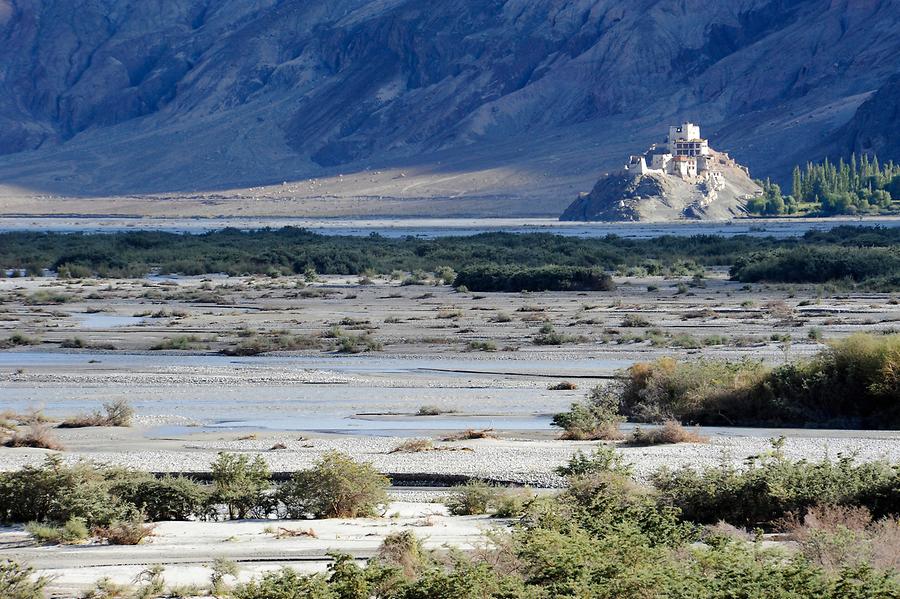
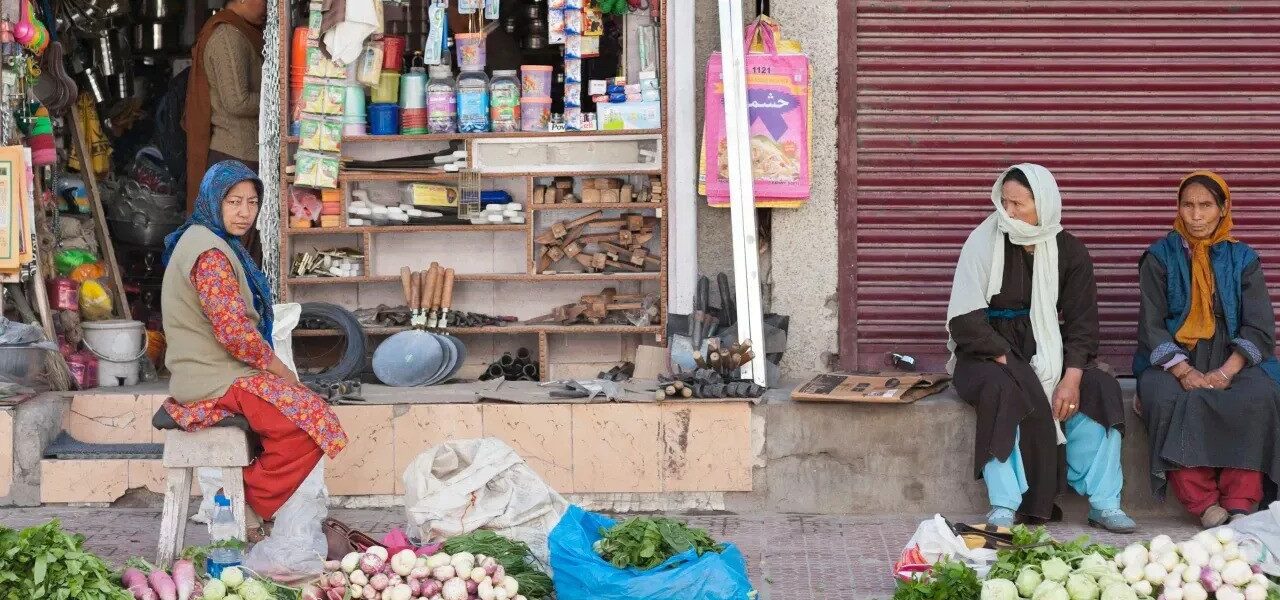
Leh, the capital of Ladakh, was a bustling center of commerce. Its market thrived with goods from as far as Persia and China. The Leh Palace stands as a symbol of the region’s rich trading past.
Located in the Nubra Valley, Panamik was a key resting place for traders. Its mineral-rich hot springs offered relief to weary travelers and their animals.
Tegar, a picturesque village on the banks of the Nubra River, served as a staging ground for caravans. Traders would prepare for the treacherous journey ahead, exchanging supplies and information.
The Silk Road was not merely a conduit for goods but also ideas and beliefs. Along Ladakh’s trade routes:
Traversing Ladakh’s trade routes was no easy feat. Traders encountered:
Ladakh ancient trade routes
Ladakh ancient trade routes | The journey through Ladakh mirrors the very essence of unraveling unknown horizons, as its dramatic landscapes and unique cultural identity awaken the deepest sense of wonder and exploration. Ladakh ancient trade routes delves into this realm where inner peace intertwines with the wild, untouched beauty of Ladakh. From the snow-capped peaks to the serene monasteries, every step in Ladakh is a step toward self-discovery. The mountains, ancient paths, and unspoken mysteries stretch before travelers, offering a meditative experience where each encounter feels both effortless and transformative. Whether it’s trekking across remote valleys or sitting quietly beside a sacred lake, Ladakh invites those who seek a deeper connection to the natural and spiritual world.

Ladakh ancient trade routes
The monasteries of Ladakh stand as living monuments to the region’s profound spiritual heritage. With origins dating back over a thousand years, these ancient structures are both places of worship and repositories of art, culture, and wisdom. Hemis Monastery, one of the largest in Ladakh, is renowned for its annual festival, featuring colorful mask dances performed by monks. The history of these monasteries reflects Ladakh’s role as a crossroads between India, Tibet, and Central Asia, where religious and cultural influences have intertwined over the centuries.
The Tibetan Buddhist influence is especially evident in the architecture and daily life of the monks. Prayer wheels, intricate murals, and the soft hum of chants fill the air as visitors explore the monastery grounds. Each monastery, from the remote Lamayuru to the awe-inspiring Thiksey, offers a window into the spiritual heart of Ladakh. These centers of meditation, learning, and community life continue to thrive, preserving traditions that have shaped Ladakh for generations.
Why Visit Ladakh for Ladakh ancient trade routes?
Ladakh is a destination that transcends mere travel. It offers a journey that touches both the outer and inner landscapes, making it a perfect setting for those who seek to unravel their own unknown horizons. The region’s breathtaking scenery—from towering mountain ranges to hidden valleys—provides not just an escape but a space for contemplation and growth. Ladakh’s culture, deeply rooted in Buddhist practices, invites visitors to reflect on their own lives and the world around them.
Ladakh’s people, known for their warmth and hospitality, add to the richness of the experience. Villages like Sumda Chun and the legendary Nubra Valley introduce travelers to a way of life that is intricately connected to nature and spirituality. Staying in local homestays allows for immersive experiences where one can learn about traditional Ladakhi customs, share meals made from local produce, and participate in community rituals.

Beyond its natural beauty, Ladakh offers a unique opportunity to explore oneself. The vastness of the region’s plateaus and the clarity of its skies seem to mirror the vastness of the human spirit. Whether it’s standing atop a mountain pass at 18,000 feet or meditating in a centuries-old monastery, Ladakh helps unravel the unknown horizons within each traveler.
Finding the Best Ladakh ancient trade routes in Ladakh
Finding the best places in Ladakh to experience “Ladakh ancient trade routes” involves venturing off the beaten path. Ladakh’s lesser-known treks, such as those leading to secluded monasteries or high-altitude lakes, offer unparalleled opportunities for solitude and reflection. The Markha Valley trek, for instance, takes travelers through verdant valleys, ancient villages, and high-altitude passes, allowing for both physical and spiritual exploration.
Ladakh’s iconic lakes, including Pangong Tso and Tso Moriri, are ideal spots for quiet contemplation. Their still waters reflect the sky, creating a mesmerizing landscape that feels timeless and infinite. Sitting beside these lakes, especially at dawn or dusk, brings an overwhelming sense of peace and connection with nature.

For those interested in Ladakh’s spiritual heritage, exploring monasteries such as Alchi, Phyang, or Diskit can be a transformative experience. These sites are not just places of worship but also centers of art, philosophy, and wisdom. Visiting these monasteries, with their ancient murals and intricate statues, offers insight into Ladakh’s rich cultural tapestry.
Ladakh’s Atmosphere and Ladakh ancient trade routes
Ladakh’s atmosphere is unlike any other place on Earth. The stark contrasts between the rugged mountains and the serene, tranquil monasteries create an environment that feels both raw and sacred. The traditional decor in Ladakhi homes and religious sites reflects this balance, with mud-brick houses adorned with prayer flags and colorful thangkas (Buddhist paintings) that add warmth and spiritual meaning to the space.

The interiors of Ladakhi homes, often simple and functional, are filled with symbols of devotion. Small shrines dedicated to Buddhist deities are common, and the air is often fragrant with incense. The use of earthy materials, like stone and wood, along with brightly colored textiles, creates an inviting and peaceful space, perfect for relaxation and reflection.
Traditional Ladakh ancient trade routes
Traditional Ladakh ancient trade routes is an integral part of the region’s identity, offering a unique blend of flavors that reflect its harsh climate and remote location. Hearty, warming dishes such as thukpa (noodle soup) and momos (dumplings) provide the sustenance needed to endure Ladakh’s cold temperatures. Skyu, a thick stew made with root vegetables and barley, is another staple of the Ladakhi diet, designed to nourish both body and spirit.

Drinks like butter tea, made with yak butter and salt, are a must-try for anyone visiting Ladakh. This rich, savory drink is not only warming but also hydrating, making it essential for those venturing into the high-altitude regions of Ladakh. Chang, a local barley beer, is often enjoyed during festivals and community gatherings, adding a sense of joy and camaraderie to any occasion.
Live Cultural Ladakh ancient trade routes in Ladakh
Ladakh is home to a vibrant cultural scene, with festivals and live performances held throughout the year. The Hemis Festival, which celebrates the birth of Guru Padmasambhava, is one of the largest and most famous events in the region. Monks dressed in elaborate costumes perform cham dances, which depict the triumph of good over evil. The energy of the festival, with its bright colors, rhythmic music, and elaborate rituals, draws visitors from around the world.
Other local festivals, such as the Losar (New Year) and Ladakh Festival, provide visitors with the chance to witness traditional dance, music, and crafts that have been passed down through generations. These events are more than just entertainment; they are a celebration of Ladakh’s rich cultural heritage and its deep connection to the spiritual world.
Trekking and Outdoor Activities Ladakh ancient trade routes
Ladakh is a trekker’s paradise, offering some of the most stunning and challenging routes in the world. From the famous Ladakh ancient trade routes, which follows the frozen Zanskar River, to lesser-known routes like the Sham Valley or Nubra Valley treks, Ladakh’s landscape offers endless possibilities for adventure and discovery. The high-altitude passes, such as Khardung La and Chang La, offer breathtaking views of snow-capped peaks and sprawling valleys.

Wildlife enthusiasts will also find Ladakh ancient trade routes to be a haven for rare species such as the snow leopard, Himalayan blue sheep, and the Tibetan wild ass. Winter expeditions to spot the elusive snow leopard in the Hemis National Park are gaining popularity among wildlife photographers and conservationists alike.
The Importance of Preserving Ladakh’s Ladakh ancient trade routes
Ladakh’s rich cultural and environmental Ladakh ancient trade routes is under increasing threat from climate change and mass tourism. Preserving this unique region requires careful attention to sustainable tourism practices. Choosing eco-friendly accommodations, supporting local businesses, and participating in community-led conservation efforts are just a few ways that visitors can contribute to the preservation of Ladakh’s natural and cultural heritage.
Ladakh’s people have a long history of living in harmony with their environment, practicing sustainable agriculture, and maintaining a deep spiritual connection to the land. Visitors are encouraged to follow the same principles, leaving no trace and respecting the fragile ecosystems that make Ladakh so special.
Etiquette and Tips for Visiting Ladakh ancient trade routes
Before visiting Ladakh, it’s essential to understand and respect the region’s customs and traditions. As a deeply spiritual place, Ladakh requires visitors to dress modestly, especially when visiting monasteries or attending religious ceremonies. Always ask for permission before taking photographs inside monasteries or of local people.
Medical Ladakh ancient trade routes
Spa trail Ladakh ancient trade routes
Ladakh ancient trade routes

When Ladakh ancient trade routes, remember to stay on designated paths to avoid damaging fragile ecosystems. Tipping is appreciated but not expected in most settings, and it’s important to carry cash, as many remote areas do not accept credit cards. Lastly, be mindful of altitude sickness and take the necessary precautions when traveling to higher elevations.
Conclusion: Enjoying Ladakh ancient trade routes in Ladakh
Ladakh is a place where the physical and spiritual worlds converge, offering travelers a journey unlike any other. Whether you’re trekking across high-altitude deserts, exploring ancient monasteries, or simply sitting in quiet reflection by a mountain lake, Ladakh invites you to unravel your own unknown horizons. By respecting the region’s traditions and practicing sustainable tourism, you help ensure that Ladakh’s beauty and cultural richness will be preserved for future generations to explore and enjoy.